
Full text loading...
Phylogeny, host association and genome size in the Lactobacillaceae . The phylogenetic tree of 287 unique species and 15 strains with unassigned species was built using concatenated alignment of amino acid sequences of core genes, produced by SCARAP (https://journals.asm.org/doi/10.1128/msystems.00264-19) as an input into IQ-TREE2 (https://academic.oup.com/mbe/article/37/5/1530/5721363) with model parameters are described in [ 2 ]. Coloured branches represent species divisions established in [ 2 ]. Coloured taxon labels indicate major clades and recently established genera. The solid circles by the species names represent genome sizes. The coloured bands on the outer ring indicate the typical habitat based on data in [ 2 ].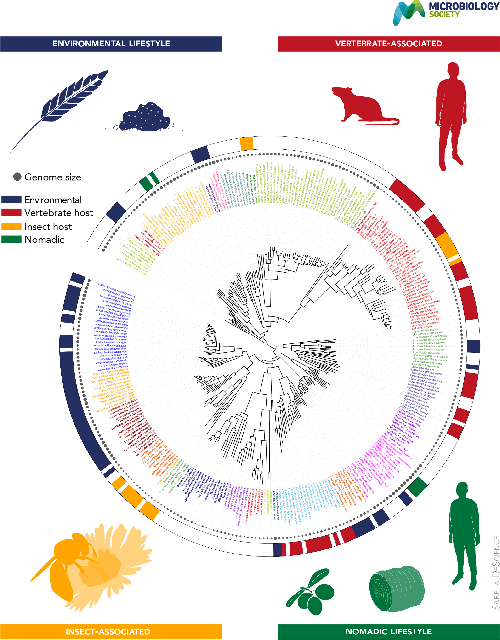
The bacterial family Lactobacillaceae (the lactobacilli) occupy a unique role in microbiology due to their beneficial role in both human cultural history and biology, from the food preservation of hunter gatherers-turned-farmers, through the prevention of scurvy in seafarers exploring new worlds, and the health-promoting properties of species that colonize the human body as well as animals that are important for agriculture and pollination. The almost bewildering phenotypic and genomic complexity of the former genus Lactobacillus was recently reconciled with molecular taxonomy and phylogeny to establish robust genera comprising the Lactobacillaceae , whose main features are summarized in this Microbe Profile.