 -
Volume 150,
Issue 8,
2004
-
Volume 150,
Issue 8,
2004
Volume 150, Issue 8, 2004
- Pathogens And Pathogenicity
-
-
-
The Candida albicans pH-regulated KER1 gene encodes a lysine/glutamic-acid-rich plasma-membrane protein that is involved in cell aggregation
More LessImmunoscreening of a Candida albicans cDNA library with a polyclonal germ-tube-specific antibody (pAb anti-gt) resulted in the isolation of a gene encoding a lysine/glutamic-acid-rich protein, which was consequently designated KER1. The nucleotide and deduced amino acid sequences of this gene displayed no significant homology with any other known sequence. KER1 encodes a 134 kDa lysine (14·5 %)/glutamic acid (16·7 %) protein (Ker1p) that contains two potential transmembrane segments. KER1 was expressed in a pH-conditional manner, with maximal expression at alkaline pH and lower expression at pH 4·0, and was regulated by RIM101. A Δker1/Δker1 null mutant grew normally but was hyperflocculant under germ-tube-inducing conditions, yet this behaviour was also observed in stationary-phase cells grown under other incubation conditions. Western blotting analysis of different subcellular fractions, using as a probe a monospecific polyclonal antibody raised against a highly antigenic domain of Ker1p (pAb anti-Ker1p), revealed the presence of a 134 kDa band in the purified plasma-membrane fraction from the wild-type strain that was absent in the homologous preparation from Δker1/Δker1 mutant. The pattern of cell-wall protein and mannoprotein species released by digestion with β-glucanases, reactive towards pAbs anti-gt and anti-Ker1p, as well as against concanavalin A, was also different in the Δker1/Δker1 mutant. Mutant strains also displayed an increased cell-surface hydrophobicity and sensitivity to Congo red and Calcofluor white. Overall, these findings indicate that the mutant strain was affected in cell-wall composition and/or structure. The fact that the ker1 mutant had attenuated virulence in systemic mouse infections suggests that this surface protein is also important in host–fungus interactions.
-
-
-
-
Expression of mptC of Listeria monocytogenes induces sensitivity to class IIa bacteriocins in Lactococcus lactis
More LessSensitivity to class IIa bacteriocins from lactic acid bacteria was recently associated with the mannose phosphotransferase system (PTS) permease,
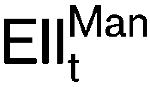 , in Listeria monocytogenes. To assess the involvement of this protein complex in class IIa bacteriocin activity, the mptACD operon, encoding
, in Listeria monocytogenes. To assess the involvement of this protein complex in class IIa bacteriocin activity, the mptACD operon, encoding 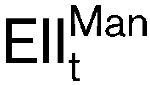 , was heterologously expressed in an insensitive species, namely Lactococcus lactis, using the NICE double plasmid system. Upon induction of the cloned operon, the recombinant Lc. lactis became sensitive to leucocin A. Pediocin PA-1 and enterocin A also showed inhibitory activity against Lc. lactis cultures expressing mptACD. Furthermore, the role of the three genes of the mptACD operon was investigated. Derivative plasmids containing various combinations of these three genes were made from the parental mptACD plasmid by divergent PCR. The results showed that expression of mptC alone is sufficient to confer sensitivity to class IIa bacteriocins in Lc. lactis.
, was heterologously expressed in an insensitive species, namely Lactococcus lactis, using the NICE double plasmid system. Upon induction of the cloned operon, the recombinant Lc. lactis became sensitive to leucocin A. Pediocin PA-1 and enterocin A also showed inhibitory activity against Lc. lactis cultures expressing mptACD. Furthermore, the role of the three genes of the mptACD operon was investigated. Derivative plasmids containing various combinations of these three genes were made from the parental mptACD plasmid by divergent PCR. The results showed that expression of mptC alone is sufficient to confer sensitivity to class IIa bacteriocins in Lc. lactis.
-
-
-
Attenuated virulence and protective efficacy of a Burkholderia pseudomallei bsa type III secretion mutant in murine models of melioidosis
More LessMelioidosis is a severe infectious disease of animals and humans caused by the Gram-negative intracellular pathogen Burkholderia pseudomallei. An Inv/Mxi-Spa-like type III protein secretion apparatus, encoded by the B. pseudomallei bsa locus, facilitates bacterial invasion of epithelial cells, escape from endocytic vesicles and intracellular survival. This study investigated the role of the Bsa type III secretion system in the pathogenesis of melioidosis in murine models. B. pseudomallei bipD mutants, lacking a component of the translocation apparatus, were found to be significantly attenuated following intraperitoneal or intranasal challenge of BALB/c mice. Furthermore, a bipD mutant was attenuated in C57BL/6 IL-12 p40−/− mice, which are highly susceptible to B. pseudomallei infection. Mutation of bipD impaired bacterial replication in the liver and spleen of BALB/c mice in the early stages of infection. B. pseudomallei mutants lacking either the type III secreted guanine nucleotide exchange factor BopE or the putative effectors BopA or BopB exhibited varying degrees of attenuation, with mutations in bopA and bopB causing a significant delay in median time to death. This indicates that bsa-encoded type III secreted proteins may act in concert to determine the outcome of B. pseudomallei infection in mice. Mice inoculated with the B. pseudomallei bipD mutant were partially protected against subsequent challenge with wild-type B. pseudomallei. However, immunization of mice with purified BipD protein was not protective.
-
-
-
Identification of an extracellular matrix protein adhesin, EmaA, which mediates the adhesion of Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans to collagen
More LessActinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans is an aetiologic agent in the development of periodontal and some systemic diseases in humans. This pathogen localizes to the underlying connective tissue of the oral cavity in individuals with periodontal disease. The adhesion of A. actinomycetemcomitans to extracellular matrix components of the connective tissue prompted this study to identify gene products mediating the interaction of A. actinomycetemcomitans to these molecules. A transposon mutagenesis system was optimized for use in A. actinomycetemcomitans and used to generate an insertional mutant library. A total of 2300 individual insertion transposon mutants were screened for changes in the adhesion to collagen and fibronectin. Mutants were identified which exhibited the following phenotypes: a decrease in collagen binding; a decrease in fibronectin binding; a decrease in binding to both proteins; and an increase in binding to both collagen and fibronectin. The identification of mutants defective in adhesion to the individual proteins indicates that distinct adhesins are expressed by this organism. Molecular analysis of these mutants implicated 11 independent loci in protein adhesion. One gene, emaA, is likely to encode a direct mediator of collagen adhesion, based on predicted protein features homologous to the collagen-binding protein YadA of Yersinia enterocolitica. EmaA was localized to the outer membrane, as expected for an adhesin. Reduction in fibronectin adhesion appeared to be influenced by abrogation of proteins involved in molybdenum-cofactor biosynthesis. Several other loci identified as reducing or increasing adhesion to both collagen and fibronectin are suggested to be involved in regulatory cascades that promote or repress expression of collagen and fibronectin adhesins. Collectively, the results support the hypothesis that A. actinomycetemcomitans host colonization involves afimbrial adhesins for extracellular matrix proteins, and that the expression of adhesion is modulated by global regulatory mechanisms.
-
-
-
Genetic and functional analysis of the cytK family of genes in Bacillus cereus
More LessCytK is a pore-forming toxin of Bacillus cereus that has been linked to a case of necrotic enteritis. PCR products of the expected size were generated with cytK primers in 13 of 29 strains. Six strains were PCR-positive for the related gene hly-II, which encodes haemolysin II, a protein that is 37 % identical to the original CytK. Five of the strains were positive for both genes. The DNA sequences of putative cytK genes from three positive strains were determined, and the deduced amino acid sequences were 89 % identical to that of the original CytK. The authors have designated this new cytK variant cytK-2, and refer to the original cytK as cytK-1. The CytK-2 proteins from these three strains were isolated, and their identity was verified by N-terminal sequencing. blast analysis using the cytK-2 gene sequences revealed very high homology with two cytK-2 sequences in the genomes of B. cereus strains ATCC 14579 and ATCC 10987. The differences between CytK-1 and the CytK-2 proteins were clustered to certain regions of the proteins. The isolated CytK-2 proteins were haemolytic and toxic towards human intestinal Caco-2 cells and Vero cells, although their toxicity was about 20 % of that of CytK-1. Both native and recombinant CytK-2 proteins from B. cereus 1230-88 were able to form pores in planar lipid bilayers, but the majority of the channels observed were of lower conductance than those created by CytK-1. It is likely that CytK-2 toxins contribute to the enterotoxicity of several strains of B. cereus, although not all of the CytK-2 toxins may be as harmful as the CytK-1 originally isolated.
-
-
-
Expression of bacteriophage ϕEa1h lysozyme in Escherichia coli and its activity in growth inhibition of Erwinia amylovora
More LessA 3·3 kb fragment from Erwinia amylovora phage ϕEa1h in plasmid pJH94 was previously characterized and found to contain an exopolysaccharide depolymerase (dpo) gene and two additional ORFs encoding 178 and 119 amino acids. ORF178 (lyz) and ORF119 (hol) were found to overlap by 19 bp and they resembled genes encoding lysozymes and holins. In nucleotide sequence alignments, lyz had structurally conserved regions with residues important for lysozyme function. The lyz gene was cloned into an expression vector and expressed in Escherichia coli. Active lysozyme was detected only when E. coli cells with the lyz gene and a kanamycin-resistance cassette were grown in the presence of kanamycin. Growth of Erw. amylovora was inhibited after addition of enzyme exceeding a threshold for lysozyme to target cells. When immature pears were soaked in lysates of induced cells, symptoms such as ooze formation and necrosis were retarded or inhibited after inoculation with Erw. amylovora.
-
-
-
Green fluorescent protein (GFP) as a vital marker for pathogenic development of the dermatophyte Trichophyton mentagrophytes
More LessSkin infections by dermatophytes of the genus Trichophyton are widespread, but methods to investigate the molecular basis of pathogenicity are only starting to be developed. The initial stages of growth on the host can only be studied by electron microscopy, which requires fixing the tissue. This paper shows that restriction-enzyme-mediated integration (REMI) provides stable expression of the green fluorescent protein (GFP) in a clinical isolate of Trichophyton mentagrophytes. Under control of a constitutively active fungal promoter, GFP renders the hyphae fluorescent both in culture and in a recently developed model using human skin explants. Stages of infection and penetration into the skin layers were visualized by confocal microscopy. The stages of infection can thus be followed using GFP as a vital marker, and this method will also provide, for the first time, a means to follow gene expression during infection of skin by dermatophyte fungi.
-
- Physiology
-
-
-
The impact of different intensities of green light on the bacteriochlorophyll homologue composition of the chlorobiaceae Prosthecochloris aestuarii and Chlorobium phaeobacteroides
More LessMembers of the Chlorobiaceae and Chloroflexaceae are unique among the phototrophic micro-organisms in having a remarkably rich chlorophyll pigment diversity. The physiological regulation of this diversity and its ecological implications are still enigmatic. The bacteriochlorophyll composition of the chlorobiaceae Prosthecochloris aestuarii strain CE 2404 and Chlorobium phaeobacteroides strain UdG 6030 was therefore studied by both HPLC with photodiode array (PDA) detection and liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS). These strains were grown in liquid cultures under green light (480–615 nm) at different light intensities (0·2–55·7 μmol photons m−2 s−1), simulating the irradiance regime at different depths of the water column of deep lakes. The specific growth rates of Ptc. aestuarii under green light achieved a maximum of 0·06 h−1 at light intensities exceeding 6 μmol photons m−2 s−1, lower than the maximum observed under white light (approx. 0·1 h−1). The maximal growth rates of Chl. phaeobacteroides under green light were slightly higher (0·07 h−1) than observed for Ptc. aestuarii and were achieved at 3·5 and 4·3 μmol photons m−2 s−1. LC-MS/MS analysis of pigment extracts revealed most (>90 %) BChl c homologues of Ptc. aestuarii to be esterified with farnesol. The homologues differed in mass by multiples of 14 Da, reflecting different alkyl subsituents at positions C-8 and C-12 on the tetrapyrrole macrocycle. The relative proportions of the individual homologues varied only slightly among different light intensities. The specific content of BChl c was maximal at 3–5 μmol photons m−2 s−1 [400±150 nmol BChl c (mg protein)−1]. In the case of Chl. phaeobacteroides, the specific content of BChl e was maximal at 4·3 μmol photons m−2 s−1 [115 nmol BChl e (mg protein)−1], and this species was characterized by high carotenoid (isorenieratene) contents. The major BChl e forms were esterified with a range of isoprenoid and straight-chain alcohols. The major isoprenoid alcohols comprised mainly farnesol and to a lesser extent geranylgeraniol. The straight-chain alcohols included C15, C15 : 1, C16, C16 : 1 and C17. Interestingly, the proportion of straight alkyl chains over isoprenoid esterified side chains shifted markedly with increasing light intensity: the isoprenoid side chains dominated at low light intensities, while the straight-chain alkyl substituents dominated at higher light intensities. The authors propose that this phenomenon may be explained as a result of changing availability of reducing power, i.e. the highly reduced straight-chain alcohols have a higher biosynthetic demand for NADPH2 than the polyunsaturated isoprenoid with the same number of carbon atoms.
-
-
- Plant-Microbe Interactions
-
-
-
Topological and deletion analysis of CorS, a Pseudomonas syringae sensor kinase
More LessA modified two-component regulatory system consisting of two response regulators, CorR and CorP, and the histidine protein kinase CorS, regulates the thermoresponsive production of the phytotoxin coronatine (COR) in Pseudomonas syringae PG4180. COR is produced at the virulence-promoting temperature of 18 °C, but not at 28 °C, the optimal growth temperature of PG4180. Assuming that the highly hydrophobic N-terminus of CorS might be involved in temperature-signal perception, the membrane topology of CorS was determined using translational phoA and lacZ fusions, leading to a topological model for CorS with six transmembrane domains (TMDs). Interestingly, three PhoA fusions located downstream of the sixth TMD showed a thermoresponsive phenotype. Enzymic activity, immunoblot, and protease-sensitivity assays were performed to localize the CorS derivatives, to analyse the expression level of hybrid proteins and to examine the model. In-frame deletions of the last four, or all six TMDs gave rise to non-functional CorS. The results indicated that the transmembrane region is important for CorS to function as a temperature sensor, and that the membrane topology of CorS might be involved in signal perception.
-
-
-
-
AlgR functions in algC expression and virulence in Pseudomonas syringae pv. syringae
More LessPseudomonas syringae pv. syringae strain FF5 is a phytopathogen associated with a rapid dieback on ornamental pear trees. P. syringae and the human pathogen Pseudomonas aeruginosa produce the exopolysaccharide alginate, a copolymer of mannuronic and guluronic acid. In P. aeruginosa, the response regulator AlgR (AlgR1) is required for transcription of algC and algD, which encode key enzymes in the alginate biosynthetic pathway. In P. syringae FF5, however, algR is not required for the activation of algD. Interestingly, algR mutants of P. syringae remain nonmucoid, indicating an undefined role for this response regulator in alginate biosynthesis. In the current study, the algC promoter region was cloned from P. syringae pv. syringae strain FF5, and sequence analysis of the algC promoter indicated the presence of potential binding sites for AlgR and σ 54, the alternative sigma factor encoded by rpoN. The algC promoter from P. syringae FF5 (PsalgC) was cloned upstream of a promoterless glucuronidase gene (uidA), and the PsalgC–uidA transcriptional fusion was used to monitor algC expression in strains FF5.32 (algR mutant of P. syringae FF5) and PG4180.K2 (rpoN mutant of P. syringae pv. glycinea PG4180). Expression of the PsalgC–uidA fusion was fourfold lower in both the algR and rpoN mutants as compared to respective wild-type strains, indicating that both AlgR and σ 54 are required for full activation of algC transcription in P. syringae pv. syringae. AlgR from P. syringae was successfully overproduced in Escherichia coli as a C-terminal translational fusion to the maltose-binding protein (MBP). Gel shift experiments indicated that MBP–AlgR binds strongly to the algC promoter region. Biological assays demonstrated that the algR mutant was significantly impaired in both pathogenicity and epiphytic fitness as compared to the wild-type strain. These results, along with the gene expression studies, indicate that AlgR has a positive role in the activation of algC in P. syringae and contributes to both virulence and epiphytic fitness. Furthermore, the symptoms observed with wild-type P. syringae FF5 suggest that this strain can move systemically in leaf tissue, and that a functional copy of algR is required for systemic movement.
-
- Theoretical Microbiology
-
-
-
Biofilms promote altruism
More LessThe origin of altruism is a fundamental problem in evolution, and the maintenance of biodiversity is a fundamental problem in ecology. These two problems combine with the fundamental microbiological question of whether it is always advantageous for a unicellular organism to grow as fast as possible. The common basis for these three themes is a trade-off between growth rate and growth yield, which in turn is based on irreversible thermodynamics. The trade-off creates an evolutionary alternative between two strategies: high growth yield at low growth rate versus high growth rate at low growth yield. High growth yield at low growth rate is a case of an altruistic strategy because it increases the fitness of the group by using resources economically at the cost of decreased fitness, or growth rate, of the individual. The group-beneficial behaviour is advantageous in the long term, whereas the high growth rate strategy is advantageous in the short term. Coexistence of species requires differences between their niches, and niche space is typically divided into four ‘axes' (time, space, resources, predators). This neglects survival strategies based on cooperation, which extend the possibilities of coexistence, arguing for the inclusion of cooperation as the fifth ‘axis’. Here, individual-based model simulations show that spatial structure, as in, for example, biofilms, is necessary for the origin and maintenance of this ‘primitive’ altruistic strategy and that the common belief that growth rate but not yield decides the outcome of competition is based on chemostat models and experiments. This evolutionary perspective on life in biofilms can explain long-known biofilm characteristics, such as the structural organization into microcolonies, the often-observed lack of mixing among microcolonies, and the shedding of single cells, as promoting the origin and maintenance of the altruistic strategy. Whereas biofilms enrich altruists, enrichment cultures, microbiology's paradigm for isolating bacteria into pure culture, select for highest growth rate.
-
-
Volumes and issues
-
Volume 170 (2024)
-
Volume 169 (2023)
-
Volume 168 (2022)
-
Volume 167 (2021)
-
Volume 166 (2020)
-
Volume 165 (2019)
-
Volume 164 (2018)
-
Volume 163 (2017)
-
Volume 162 (2016)
-
Volume 161 (2015)
-
Volume 160 (2014)
-
Volume 159 (2013)
-
Volume 158 (2012)
-
Volume 157 (2011)
-
Volume 156 (2010)
-
Volume 155 (2009)
-
Volume 154 (2008)
-
Volume 153 (2007)
-
Volume 152 (2006)
-
Volume 151 (2005)
-
Volume 150 (2004)
-
Volume 149 (2003)
-
Volume 148 (2002)
-
Volume 147 (2001)
-
Volume 146 (2000)
-
Volume 145 (1999)
-
Volume 144 (1998)
-
Volume 143 (1997)
-
Volume 142 (1996)
-
Volume 141 (1995)
-
Volume 140 (1994)
-
Volume 139 (1993)
-
Volume 138 (1992)
-
Volume 137 (1991)
-
Volume 136 (1990)
-
Volume 135 (1989)
-
Volume 134 (1988)
-
Volume 133 (1987)
-
Volume 132 (1986)
-
Volume 131 (1985)
-
Volume 130 (1984)
-
Volume 129 (1983)
-
Volume 128 (1982)
-
Volume 127 (1981)
-
Volume 126 (1981)
-
Volume 125 (1981)
-
Volume 124 (1981)
-
Volume 123 (1981)
-
Volume 122 (1981)
-
Volume 121 (1980)
-
Volume 120 (1980)
-
Volume 119 (1980)
-
Volume 118 (1980)
-
Volume 117 (1980)
-
Volume 116 (1980)
-
Volume 115 (1979)
-
Volume 114 (1979)
-
Volume 113 (1979)
-
Volume 112 (1979)
-
Volume 111 (1979)
-
Volume 110 (1979)
-
Volume 109 (1978)
-
Volume 108 (1978)
-
Volume 107 (1978)
-
Volume 106 (1978)
-
Volume 105 (1978)
-
Volume 104 (1978)
-
Volume 103 (1977)
-
Volume 102 (1977)
-
Volume 101 (1977)
-
Volume 100 (1977)
-
Volume 99 (1977)
-
Volume 98 (1977)
-
Volume 97 (1976)
-
Volume 96 (1976)
-
Volume 95 (1976)
-
Volume 94 (1976)
-
Volume 93 (1976)
-
Volume 92 (1976)
-
Volume 91 (1975)
-
Volume 90 (1975)
-
Volume 89 (1975)
-
Volume 88 (1975)
-
Volume 87 (1975)
-
Volume 86 (1975)
-
Volume 85 (1974)
-
Volume 84 (1974)
-
Volume 83 (1974)
-
Volume 82 (1974)
-
Volume 81 (1974)
-
Volume 80 (1974)
-
Volume 79 (1973)
-
Volume 78 (1973)
-
Volume 77 (1973)
-
Volume 76 (1973)
-
Volume 75 (1973)
-
Volume 74 (1973)
-
Volume 73 (1972)
-
Volume 72 (1972)
-
Volume 71 (1972)
-
Volume 70 (1972)
-
Volume 69 (1971)
-
Volume 68 (1971)
-
Volume 67 (1971)
-
Volume 66 (1971)
-
Volume 65 (1971)
-
Volume 64 (1970)
-
Volume 63 (1970)
-
Volume 62 (1970)
-
Volume 61 (1970)
-
Volume 60 (1970)
-
Volume 59 (1969)
-
Volume 58 (1969)
-
Volume 57 (1969)
-
Volume 56 (1969)
-
Volume 55 (1969)
-
Volume 54 (1968)
-
Volume 53 (1968)
-
Volume 52 (1968)
-
Volume 51 (1968)
-
Volume 50 (1968)
-
Volume 49 (1967)
-
Volume 48 (1967)
-
Volume 47 (1967)
-
Volume 46 (1967)
-
Volume 45 (1966)
-
Volume 44 (1966)
-
Volume 43 (1966)
-
Volume 42 (1966)
-
Volume 41 (1965)
-
Volume 40 (1965)
-
Volume 39 (1965)
-
Volume 38 (1965)
-
Volume 37 (1964)
-
Volume 36 (1964)
-
Volume 35 (1964)
-
Volume 34 (1964)
-
Volume 33 (1963)
-
Volume 32 (1963)
-
Volume 31 (1963)
-
Volume 30 (1963)
-
Volume 29 (1962)
-
Volume 28 (1962)
-
Volume 27 (1962)
-
Volume 26 (1961)
-
Volume 25 (1961)
-
Volume 24 (1961)
-
Volume 23 (1960)
-
Volume 22 (1960)
-
Volume 21 (1959)
-
Volume 20 (1959)
-
Volume 19 (1958)
-
Volume 18 (1958)
-
Volume 17 (1957)
-
Volume 16 (1957)
-
Volume 15 (1956)
-
Volume 14 (1956)
-
Volume 13 (1955)
-
Volume 12 (1955)
-
Volume 11 (1954)
-
Volume 10 (1954)
-
Volume 9 (1953)
-
Volume 8 (1953)
-
Volume 7 (1952)
-
Volume 6 (1952)
-
Volume 5 (1951)
-
Volume 4 (1950)
-
Volume 3 (1949)
-
Volume 2 (1948)
-
Volume 1 (1947)
Most Read This Month


