
Full text loading...
Summary: Methods by which the R-factor 1818 was transferred from Escherichia coli K12 to different species of Gram-negative bacteria are described. Possession of 1818 resulted in the production of similar amounts of R-factor specific penicillinase per organism in E. coli, Serratia marcescens, Alkalescens sp. and Aerobacter aerogenes. The Aerobacter strain produced additionally a ‘chromosomal’ penicillinase which had no influence on the level of R-factor enzyme.
Two different strains of Proteus mirabilis containing R-factor 1818 produced only about 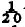 th of this penicillinase activity per bacterium Two further R-factors 7268 and TEM also specifying penicillinase were introduced into theP. mirabilis strains and enzyme activities per bacterium of about
th of this penicillinase activity per bacterium Two further R-factors 7268 and TEM also specifying penicillinase were introduced into theP. mirabilis strains and enzyme activities per bacterium of about 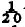 th and th, respectively, were obtained compared with those in E. coli. All organisms in cultures of P. mirabilis exhibited properties of R-factor possession and thus R-factor instability cannot explain these results. It would seem that the phenotypic expression of R-factor penicillinase genes is impaired in this species.
th and th, respectively, were obtained compared with those in E. coli. All organisms in cultures of P. mirabilis exhibited properties of R-factor possession and thus R-factor instability cannot explain these results. It would seem that the phenotypic expression of R-factor penicillinase genes is impaired in this species.

Article metrics loading...

Full text loading...
References


Data & Media loading...
