 -
Volume 58,
Issue 5,
2008
-
Volume 58,
Issue 5,
2008
Volume 58, Issue 5, 2008
- New Taxa
-
- Other Bacteria
-
-
Sulfurihydrogenibium kristjanssonii sp. nov., a hydrogen- and sulfur-oxidizing thermophile isolated from a terrestrial Icelandic hot spring
More LessThree thermophilic, aerobic, hydrogen- and sulfur-oxidizing bacteria were isolated from an Icelandic hot spring near the town of Hveragerdi and share >99 % 16S rRNA gene sequence similarity. One of these isolates, designated strain I6628T, was selected for further characterization. Strain I6628T is a motile rod, 1.5–2.5 μm long and about 0.5 μm wide. Growth occurred between 40 and 73 °C (optimally at 68 °C), at pH 5.3–7.8 (optimally at pH 6.6) and at NaCl concentrations between 0 and 0.5 % (w/v). Strain I6628T grew with H2, S0 or
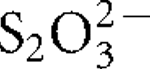 as an electron donor with O2 (up to 25 %, v/v; optimally at 4–9 %) as the sole electron acceptor. CO2 and succinate were utilized as carbon sources but no organic compounds, including succinate, could be used as an energy source. The G+C content of the genomic DNA was determined to be 28.1 mol%. Phylogenetic analysis of the 16S rRNA gene sequence indicated that strain I6628T is a member of the genus Sulfurihydrogenibium, the closest cultivated relative being the recently described strain Sulfurihydrogenibium rodmanii UZ3-5T (98.2 % sequence similarity). On the basis of the physiology and phylogeny of this organism, strain I6628T represents a novel species of the genus Sulfurihydrogenibium, for which the name Sulfurihydrogenibium kristjanssonii sp. nov. is proposed. The type strain is I6628T (=DSM 19534T =OCM 901T =ATCC BAA-1535T).
as an electron donor with O2 (up to 25 %, v/v; optimally at 4–9 %) as the sole electron acceptor. CO2 and succinate were utilized as carbon sources but no organic compounds, including succinate, could be used as an energy source. The G+C content of the genomic DNA was determined to be 28.1 mol%. Phylogenetic analysis of the 16S rRNA gene sequence indicated that strain I6628T is a member of the genus Sulfurihydrogenibium, the closest cultivated relative being the recently described strain Sulfurihydrogenibium rodmanii UZ3-5T (98.2 % sequence similarity). On the basis of the physiology and phylogeny of this organism, strain I6628T represents a novel species of the genus Sulfurihydrogenibium, for which the name Sulfurihydrogenibium kristjanssonii sp. nov. is proposed. The type strain is I6628T (=DSM 19534T =OCM 901T =ATCC BAA-1535T).
-
-
-
Singulisphaera acidiphila gen. nov., sp. nov., a non-filamentous, Isosphaera-like planctomycete from acidic northern wetlands
More LessFour novel strains of budding bacteria, designated MOB10T, PO2, MPL1015 and BG32, were isolated from acidic wetlands of northern Russia. Cells of these four strains were aerobic, non-motile spheres that occurred singly or in shapeless aggregates and attached to surfaces by means of a holdfast material. The isolates were moderately acidophilic, mesophilic organisms capable of growth between pH 4.2 and 7.5 (optimum growth at pH 5.0–6.2) and at temperatures between 4 and 33 °C (optimum growth at 20–26 °C). The strains possessed a complex intracellular membrane system that compartmentalized the cells. The major fatty acids were C16 : 0, C18 : 1 ω9c and C18 : 2 ω6c,12c. The major quinone was menaquinone-6 (MK-6). The G+C content of the DNA was 57.8–59.9 mol%. 16S rRNA gene sequence analysis showed that strains MOB10T, PO2, MPL1015 and BG32 were members of the order Planctomycetales and belonged to a phylogenetic lineage defined by the genus Isosphaera, exhibiting 90 % sequence similarity to the type strain of the thermophilic planctomycete Isosphaera pallida and 95–95.5 % sequence similarity to a taxonomically uncharacterized group of filamentous bacteria from activated sludge, ‘Nostocoida limicola’ III. However, compared with ‘Nostocoida limicola’ III and Isosphaera pallida, the new isolates from acidic wetlands were non-filamentous, unpigmented bacteria, which possessed highly distinctive phospholipid fatty acid profiles and were capable of growth and of degrading several biopolymers under acidic, microaerobic and cold conditions. The data suggest that the four isolates should be considered as representing a novel species of a new genus of the order Planctomycetales, for which the name Singulisphaera acidiphila gen. nov., sp. nov. is proposed. The type strain of Singulisphaera acidiphila is MOB10T (=ATCC BAA-1392T =VKM B-2454T =DSM 18658T).
-
-
-
Description of four novel psychrophilic, ionizing radiation-sensitive Deinococcus species from alpine environments
More LessFive psychrophilic bacterial strains were isolated from soil samples collected above the treeline of alpine environments. Phylogenetic analysis based on 16S rRNA gene sequences indicated that these organisms represent four novel species of the genus Deinococcus; levels of sequence similarity to the type strains of recognized Deinococcus species were in the range 89.3–94.7 %. Strains PO-04-20-132T, PO-04-20-144, PO-04-19-125T, ME-04-01-32T and ME-04-04-52T grew aerobically, with optimum growth at 10 °C and at pH 6–9. The major respiratory menaquinone was MK-8. The fatty acid profiles of strains PO-04-20-132T, PO-04-20-144, PO-04-19-125T and ME-04-01-32T were dominated by 16 : 1ω7c, 17 : 0 iso and 15 : 1ω6c, whereas 16 : 1ω7c, 17 : 0 cyclo and 16 : 0 predominated in strain ME-04-04-52T. The DNA G+C contents of strains PO-04-20-132T, PO-04-19-125T, ME-04-01-32T and ME-04-04-52T were 63.2, 63.1, 65.9 and 62.6 mol%, respectively. Strains PO-04-20-132T, PO-04-19-125T, ME-04-01-32T and ME-04-04-52T had gamma radiation D10 (dose required to reduce the bacterial population by 10-fold) values of ≤4 kGy. These four strains showed sensitivity to UV radiation and extended desiccation as compared with Deinococcus radiodurans. On the basis of the phylogenetic analyses, and chemotaxonomic and phenotypic data, it is proposed that strains PO-04-20-132T (=LMG 24019T=NRRL B-41950T; Deinococcus radiomollis sp. nov.), PO-04-19-125T (=LMG 24282T=NRRL B-41949T; Deinococcus claudionis sp. nov.), ME-04-01-32T (=LMG 24022T=NRRL B-41947T; Deinococcus altitudinis sp. nov.) and ME-04-04-52T (=LMG 24283T=NRRL B-41948T; Deinococcus alpinitundrae sp. nov.) represent the type strains of four novel species of the genus Deinococcus.
-
- Proteobacteria
-
-
Caenimonas koreensis gen. nov., sp. nov., isolated from activated sludge
More LessA Gram-negative, rod-shaped bacterium, designated strain EMB320T, was isolated from activated sludge performing enhanced biological phosphorus removal in a sequencing batch reactor. The isolate was strictly aerobic and non-motile. Growth was observed between 10 and 35 °C (optimum 30 °C) and between pH 6.0 and 9.0 (optimum pH 7.0–8.0). The predominant cellular fatty acids of strain EMB320T were C16 : 0, C18 : 1 ω7c and summed feature 3 (C16 : 1 ω7c and/or iso-C15 : 0 2-OH). The major polar lipids were phosphatidylethanolamine, phosphatidylglycerol and diphosphatidylglycerol. Strain EMB320T contained ubiquinone-8 (Q-8) as the major respiratory quinone system and 2-hydroxyputrescine and putrescine as the major polyamines, which suggests that it belongs to the Betaproteobacteria. The G+C content of the genomic DNA was 62.7 mol%. Comparative 16S rRNA gene sequence analysis showed that strain EMB320T formed a phyletic lineage distinct from other genera within the family Comamonadaceae. On the basis of chemotaxonomic data and molecular properties, strain EMB320T represents a novel genus and species within the family Comamonadaceae, for which the name Caenimonas koreensis sp. nov. is proposed. The type strain of Caenimonas koreensis is EMB320T (=KCTC 12616T =DSM 17982T).
-
-
-
Geobacter uraniireducens sp. nov., isolated from subsurface sediment undergoing uranium bioremediation
More LessA Gram-negative, rod-shaped, motile bacterium, strain Rf4T, which conserves energy from dissimilatory Fe(III) reduction concomitant with acetate oxidation, was isolated from subsurface sediment undergoing uranium bioremediation. The 16S rRNA gene sequence of strain Rf4T matched sequences recovered in 16S rRNA gene clone libraries constructed from DNA extracted from groundwater sampled at the same time as the source sediment. Cells of strain Rf4T were regular, motile rods, 1.2–2.0 μm long and 0.5–0.6 μm in diameter, with rounded ends. Cells had one lateral flagellum. Growth was optimal at pH 6.5–7.0 and 32 °C. With acetate as the electron donor, strain Rf4T used Fe(III), Mn(IV), anthraquinone-2,6-disulfonate, malate and fumarate as electron acceptors and reduced U(VI) in cell suspensions. With poorly crystalline Fe(III) oxide as the electron acceptor, strain Rf4T oxidized the following electron donors: acetate, lactate, pyruvate and ethanol. Phylogenetic analysis of the 16S rRNA gene sequence of strain Rf4T placed it in the genus Geobacter. Strain Rf4T was most closely related to ‘Geobacter humireducens’ JW3 (95.9 % sequence similarity), Geobacter bremensis Dfr1T (95.4 %) and Geobacter bemidjiensis BemT (95.1 %). Based on phylogenetic analysis and phenotypic differences between strain Rf4T and closely related Geobacter species, this strain is described as a representative of a novel species, Geobacter uraniireducens sp. nov. The type strain is Rf4T (=ATCC BAA-1134T =JCM 13001T).
-
-
-
Microbulbifer agarilyticus sp. nov. and Microbulbifer thermotolerans sp. nov., agar-degrading bacteria isolated from deep-sea sediment
More LessNine agar-degrading strains, designated JAMB A3T, JAMB A7, JAMB A24, JAMB A33, JAMB A94T, JAMM 0654, JAMM 0793, JAMM 1327 and JAMM 1340, were isolated from deep-sea sediment in Suruga Bay and Sagami Bay and off Kagoshima, Japan. On the basis of 16S rRNA gene sequence analysis, the strains were found to be closely affiliated with members of the genera Microbulbifer and Thalassomonas. The hybridization values for DNA–DNA relatedness between two of these strains and Microbulbifer reference strains were significantly lower than that accepted as the phylogenetic definition of a species. On the basis of their distinct taxonomic characteristics, six of the isolated strains represent two novel species of the genus Microbulbifer, for which the names Microbulbifer agarilyticus sp. nov. (type strain JAMB A3T =JCM 14708T =DSM 19200T) and Microbulbifer thermotolerans sp. nov. (type strain JAMB A94T =JCM 14709T =DSM 19189T) are proposed.
-
-
-
Methylobacterium persicinum sp. nov., Methylobacterium komagatae sp. nov., Methylobacterium brachiatum sp. nov., Methylobacterium tardum sp. nov. and Methylobacterium gregans sp. nov., isolated from freshwater
More LessEight strains, 002-165T, 002-079T, B0021T, Hojyo2, RB603B, RB677T, 002-074T and RB678, isolated from the environment of food-processing factories in Japan, were characterized using a polyphasic approach. The isolates were Gram-negative, strictly aerobic, pink-pigmented, facultatively methylotrophic, non-spore-forming rods. The chemotaxonomic characteristics of these isolates included the presence of C18 : 1 ω7c as the major cellular fatty acid and ubiquinone Q-10 as the predominant ubiquinone. The DNA G+C content was 67.1–71.1 mol%. Phylogenetic analyses of 16S rRNA and DNA gyrase B subunit (gyrB) nucleotide sequence confirmed that the eight strains belonged to the Methylobacterium clade. Moreover, a DNA–DNA hybridization analysis showed that the eight isolates represented five novel species. On the basis of their phenotypic and phylogenetic distinctiveness, the isolates represent five novel species within the genus Methylobacterium, for which the names Methylobacterium persicinum sp. nov. (type strain 002-165T =DSM 19562T =NBRC 103628T =NCIMB 14378T), Methylobacterium komagatae sp. nov. (type strain 002-079T =DSM 19563T =NBRC 103627T =NCIMB 14377T), Methylobacterium brachiatum sp. nov. (type strain B0021T =DSM 19569T =NBRC 103629T =NCIMB 14379T), Methylobacterium tardum sp. nov. (type strain RB677T =DSM 19566T =NBRC 103632T =NCIMB 14380T) and Methylobacterium gregans sp. nov. (type strain 002-074T =DSM 19564T =NBRC 103626T =NCIMB 14376T) are proposed.
-
-
-
Aurantimonas frigidaquae sp. nov., isolated from a water-cooling system
More LessA motile, short rod-shaped and yellow-pigmented bacterium, designated strain CW5T, was isolated from a water-cooling system at Gwangyang, Republic of Korea. Cells were Gram-negative, facultatively anaerobic and catalase- and oxidase-positive. The major fatty acids were C18 : 1 ω7c (64.7 %) and C16 : 0 (14.1 %). The DNA G+C content was 63.9 mol%. A phylogenetic tree based on 16S rRNA gene sequence comparison showed that strain CW5T clustered within the Aurantimonas lineage and is closely related to the type strains of Aurantimonas altamirensis (98.5 % sequence similarity) and Aurantimonas coralicida (95.7 %). The phenotypic characteristics and DNA–DNA hybridization data indicate that strain CW5T could be distinguished from the phylogenetic relatives A. altamirensis and A. coralicida. On the basis of the evidence presented in this study, strain CW5T represents a novel species of the genus Aurantimonas, for which the name Aurantimonas frigidaquae sp. nov. is proposed. The type strain is CW5T (=KCTC 12893T =JCM 14755T).
-
-
-
Salinivibrio proteolyticus sp. nov., a moderately halophilic and proteolytic species from a hypersaline lake in Iran
More LessA novel moderately halophilic, Gram-negative, curved-rod-shaped bacterium, designated strain AF-2004T, was isolated from Bakhtegan Lake, a hypersaline lake with 17 % (w/v) total salt located in the southern region of Iran. Strain AF-2004T was a facultative anaerobe, motile by one polar flagellum, non-sporulating and oxidase- and catalase-positive. It grew at salinities of 1–17 % (w/v) NaCl, showing optimal growth at 5 % (w/v). Growth occurred at 10.0–45.0 °C and pH 5.0–9.5, with optimum growth at 32.0–35.0 °C and pH 8.0–8.5. Phylogenetic analyses based on 16S rRNA gene sequence comparisons indicated that strain AF-2004T is a member of the genus Salinivibrio. Strain AF-2004T had C18 : 1 ω7c (31.6 %), C16 : 1 ω7c (22.1 %) and C16 : 0 (20.7 %) as the predominant fatty acids and Q-8 as the major respiratory lipoquinone. The DNA G+C content was 49.5 mol%, which is in the range of values for members of the genus Salinivibrio. On the basis of differentiation from Salinivibrio costicola by phenotypic and chemotaxonomic characteristics, 16S rRNA sequence analysis and DNA–DNA relatedness, it is proposed that strain AF-2004T (=DSM 19052T =CIP 109598T) should be placed in the genus Salinivibrio as the type strain of a novel species, Salinivibrio proteolyticus sp. nov.
-
-
-
Aeromonas aquariorum sp. nov., isolated from aquaria of ornamental fish
More LessDuring a survey to determine the prevalence of Aeromonas strains in water and skin of imported ornamental fish, 48 strains presumptively identified as Aeromonas were isolated but they could not be identified as members of any previously described Aeromonas species. These strains were subjected to a polyphasic approach including phylogenetic analysis derived from gyrB, rpoD and 16S rRNA gene sequencing, DNA–DNA hybridization, MALDI-TOF MS analysis, genotyping by RAPD and extensive biochemical and antibiotic susceptibility tests in order to determine their taxonomic position. Based on the results of the phylogenetic analyses and DNA–DNA hybridization data, we describe a novel species of the genus Aeromonas, for which the name Aeromonas aquariorum sp. nov. is proposed, with strain MDC47T (=DSM 18362T =CECT 7289T) as the type strain. This is the first Aeromonas species description based on isolations from ornamental fish.
-
-
-
Roseovarius aestuarii sp. nov., isolated from a tidal flat of the Yellow Sea in Korea
More LessA Gram-negative, motile, ovoid to rod-shaped bacterial strain, designated strain SMK-122T, was isolated from a Yellow Sea tidal flat located on the coast of Korea. Strain SMK-122T grew optimally at pH 7.0–8.0 and 30 °C. It contained Q-10 as the predominant ubiquinone and possessed C18 : 1 ω7c and C16 : 0 as the major fatty acids. The DNA G+C content was 58.6 mol%. A phylogenetic analysis based on 16S rRNA gene sequences showed that strain SMK-122T fell within the genus Roseovarius, being closest to Roseovarius nubinhibens ISMT; the sequence similarities with respect to Roseovarius species ranged from 94.9 to 97.3 %. The mean value for DNA–DNA relatedness between strain SMK-122T and Rva. nubinhibens DSM 15170T was 13 %. Differential phenotypic properties of SMK-122T, together with its phylogenetic and genetic distinctiveness, revealed that this strain is distinct from recognized Roseovarius species. On this basis, strain SMK-122T represents a novel species of the genus Roseovarius, for which the name Roseovarius aestuarii sp. nov. is proposed. The type strain is SMK-122T (=KCTC 22174T =CCUG 55325T).
-
-
-
Haliea salexigens gen. nov., sp. nov., a member of the Gammaproteobacteria from the Mediterranean Sea
More LessA novel aerobic, Gram-negative bacterium, designated 3X/A02/235T, was isolated from the surface of coastal waters in the north-western Mediterranean Sea. Cells were motile, straight rods, 1.6 μm long and 0.5 μm wide, and formed cream colonies on marine agar medium. The G+C content of the genomic DNA was 61 mol%. Phylogenetic analysis of the 16S rRNA gene sequence placed the strain in the class Gammaproteobacteria and within the family Alteromonadaceae. On the basis of 16S rRNA gene sequence comparisons and physiological and biochemical characteristics, this isolate represents a novel species of a novel genus, for which the name Haliea salexigens gen. nov., sp. nov. is proposed. The type strain of Haliea salexigens is 3X/A02/235T (=DSM 19537T =CIP 109602T =MOLA 286T).
-
-
-
Massilia brevitalea sp. nov., a novel betaproteobacterium isolated from lysimeter soil
More LessA Gram-negative, strictly aerobic bacterium, designated strain byr23-80T, was isolated from lysimeter soil by using a high-throughput cultivation technique. Cells of strain byr23-80T were found to be short rods that multiplied by binary fission and were motile by means of a single polar flagellum. Occasionally, two to three polar or lateral flagella were observed. The optimum growth temperature was 15 °C and the pH optimum was 7.0–7.5. The predominant cellular fatty acids were C16 : 1 ω7c (54.7 %) and C16 : 0 (21.4 %). In addition, the diagnostic fatty acids C10 : 0 3-OH and C12 : 0 2-OH were detected. Q-8 was the predominant respiratory quinone. The isolate was physiologically very versatile, using a wide range of sugars, organic acids and amino acids as single carbon and energy sources for growth. The G+C content of the genomic DNA was 65.3 mol%. Phylogenetic analyses supported the assignment of strain byr23-80T to the genus Massilia within the family Oxalobacteraceae of the class Betaproteobacteria. Within the genus, strain byr23-80T was most closely related to Massilia aurea DSM 18055T, with a 16S rRNA gene sequence similarity of 98.3 %. However, DNA–DNA hybridization revealed a pairwise similarity for the genomic DNA of only 20.1 % between strain byr23-80T and strain DSM 18055T. The novel isolate could be distinguished from the existing species Massilia timonae, Massilia dura, Massilia albidiflava, Massilia plicata, Massilia lutea and M. aurea by its significantly lower temperature optimum for growth and by the absence of gelatinase, α-galactosidase and β-galactosidase activities. On the basis of these characteristics, strain byr23-80T constitutes a novel species of the genus Massilia, for which the name Massilia brevitalea sp. nov. is proposed. The type strain is byr23-80T (=DSM 18925T=ATCC BAA-1465T).
-
-
-
Halomonas caseinilytica sp. nov., a halophilic bacterium isolated from a saline lake on the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau, China
More LessA halophilic, Gram-negative bacterial strain, designated AJ261T, which was isolated from a soil sample from a salt lake on the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau, was subjected to a polyphasic taxonomic study. The isolate grew optimally in the presence of 3–5 % NaCl and used various carbohydrates as sole carbon and energy sources. The genomic DNA G+C content was 63.0 mol%. The predominant fatty acids were C18 : 1 ω7c, C16 : 0 and C12 : 0. A phylogenetic analysis based on 16S rRNA gene sequences indicated that the isolate had the highest sequence similarity with respect to type strains of Halomonas elongata (98.2 %), Halomonas eurihalina (98.1 %) and Halomonas halmophila (97.2 %). The DNA–DNA relatedness of strain AJ261T with respect to H. elongata NBRC 15536T, H. eurihalina CGMCC 1.2318T and H. halmophila DSM 5349T was 42, 25 and 26 %, respectively. Overall, the phenotypic, genotypic and phylogenetic results demonstrate that strain AJ261T represents a novel species within the genus Halomonas, for which the name Halomonas caseinilytica is proposed. The type strain is AJ261T (=CGMCC 1.6773T =JCM 14802T).
-
- Eukaryotic Micro-Organisms
-
-
Kazachstania hellenica sp. nov., a novel ascomycetous yeast from a Botrytis-affected grape must fermentation
More LessFour ascomycetous yeast strains (D4W13, D9W2, D9W4 and D9W17T) were isolated from Botrytis-affected fermenting grape juice originating from Attica Province, Greece. Phylogenetic analysis of rRNA gene sequences (18S, 26S and 5.8S–ITS) showed that the four strains represent a distinct species within the genus Kazachstania, closely related to Kazachstania zonata NBRC 100504T and Kazachstania gamospora NBRC 11056T. Electrophoretic karyotyping and physiological analysis support the affiliation of the four strains in a novel species for which the name Kazachstania hellenica sp. nov. is proposed, with D9W17T (=CBS 10706T=NBRC 103637T) as the type strain.
-
- Other Gram-Positive Bacteria
-
-
Description of Caldalkalibacillus uzonensis sp. nov. and emended description of the genus Caldalkalibacillus
More LessStrain JW/WZ-YB58T, a thermophilic (42–64 °C), aerobic, alkalitolerant (pH25 °C 6.4–9.7), heterotrophic, sporulating, retarded-peritrichously flagellated and slightly curved rod-shaped bacterium, was isolated from the hot spring Zarvarzin II in the East Thermal Field of the Uzon Caldera, Kamchatka (Far East Russia). The isolate tolerated high concentrations of CO. The major membrane phospholipid fatty acids of JW/WZ-YB58T included iso-C15 : 0 (24.5 %), anteiso-C15 : 0 (18.3 %) and iso-C17 : 0 (17.5 %). The G+C content of the genomic DNA is 45 mol% (HPLC method). Based on 16S rRNA gene sequence analysis and physiological properties, isolate JW/WZ-YB58T (=ATCC BAA-1258T =DSM 17740T) is proposed as the type strain of Caldalkalibacillus uzonensis sp. nov. In contrast to the type species Caldalkalibacillus thermarum, a catalase-reaction-positive aerobe, C. uzonensis was catalase-reaction-negative; thus the description of the genus Caldalkalibacillus is emended to include a catalase-reaction-negative species.
-
-
-
Oceanobacillus caeni sp. nov., isolated from a Bacillus-dominated wastewater treatment system in Korea
More LessA Gram-positive, rod-shaped, spore-forming bacterium, strain S-11T, was isolated from the activated sludge of a Bacillus-dominated wastewater treatment system in South Korea and was characterized using a polyphasic approach in order to determine its taxonomic position. Cells (0.5–0.6×2.0–2.2 μm) were motile by means of a single subpolar flagellum. They bore ellipsoidal endospores that lay in a central position in swollen sporangia. Phylogenetic analysis based on 16S rRNA gene sequences revealed that strain S-11T was a member of the genus Oceanobacillus. 16S rRNA gene sequence similarity values and DNA–DNA relatedness of strain S-11T to the type strains of other Oceanobacillus species were less than 96.2 and 66.0 %, respectively. Strain S-11T showed distinct differences in the G+C content of the genomic DNA (33.6 mol%). The major cellular fatty acids were iso-C14 : 0, iso-C15 : 0, anteiso-C15 : 0 and iso-C16 : 0. The major isoprenoid quinone was MK-7. There were also some physiological differences in comparison with the type strains of Oceanobacillus species: tests for production of acetoin and acid production from dulcitol, erythritol, myo-inositol and sorbitol were positive. The results of DNA–DNA hybridization and physiological and biochemical tests allowed genotypic and phenotypic differentiation of strain S-11T from the six Oceanobacillus species and subspecies with validly published names. Strain S-11T therefore represents a novel species, for which the name Oceanobacillus caeni sp. nov. is proposed, with the type strain S-11T (=KCTC 13061T =CCUG 53534T =CIP 109363T).
-
-
-
Paenibacillus ginsengihumi sp. nov., a bacterium isolated from soil in a ginseng field
More LessStrain DCY16T, a Gram-positive, spore-forming, rod-shaped, motile bacterium, was isolated from soil and characterized in order to determine its taxonomic position. 16S rRNA gene sequence analysis revealed that strain DCY16T belonged to the genus Paenibacillus; highest sequence similarities were with Paenibacillus validus JCM 9077T (94.4 %), P. chinjuensis WN9T (94.4 %), P. naphthalenovorans DSM 14203T (94.2 %), P. ehimensis KCTC 3748T (92.8 %) and P. elgii KCTC 10016BPT (92.4 %). Chemotaxonomic data revealed that strain DCY16T possessed menaquinone MK-7 and the predominant fatty acids were C15 : 0 anteiso, C17 : 0 anteiso, C16 : 0 and C16 : 0 iso. The DNA G+C content of strain DCY16T was 50.9 mol%. Results of physiological and biochemical tests clearly demonstrated that strain DCY16T represents a distinct Paenibacillus species. Based on these data, DCY16T (=KCTC 13141T =JCM 14928T) should be classified as the type strain of a novel species, for which the name Paenibacillus ginsengihumi sp. nov. is proposed.
-
-
-
Desulfosporosinus hippei sp. nov., a mesophilic sulfate-reducing bacterium isolated from permafrost
More LessThe sulfate-reducing strain 343T was isolated from ancient permafrost deposits in Siberia, Russia. Based on 16S rRNA gene sequence analyses, this strain was closely related to Desulfosporosinus species, showing 97.9 % 16S rRNA gene sequence similarity to Desulfosporosinus meridiei DSM 13257T, 97.6 % similarity to Desulfosporosinus auripigmenti DSM 13351T, 97.2 % similarity to Desulfosporosinus lacus DSM 15449T and 96.2 % similarity to Desulfosporosinus orientis DSM 765T. The strain was found to contain b-type cytochromes and to reduce only sulfate and thiosulfate using lactate as an electron donor but not sulfite, elemental sulfur, fumarate, nitrate or Fe(III). These data, considered in conjunction with DNA–DNA hybridization data, cell-wall chemotaxonomy and data on physiology, support recognition of strain 343T as representing a distinct and novel species within the genus Desulfosporosinus, namely Desulfosporosinus hippei sp. nov., with the type strain 343T (=DSM 8344T =VKM B-2003T).
-
- Evolution, Phylogeny And Biodiversity
-
-
-
Phylogenetic relationships amongst the saltwater members of the genus Bacteriovorax using rpoB sequences and reclassification of Bacteriovorax stolpii as Bacteriolyticum stolpii gen. nov., comb. nov.
More LessMembers of the saltwater genus Bacteriovorax, formerly known as the marine Bdellovibrio, are obligate predatory bacteria that prey selectively on other Gram-negative bacteria. Previous phylogenetic analysis based on the 16S rRNA genes of saltwater Bacteriovorax isolates from environmental samples revealed 11 distinct phylogenetic clusters based on ≥96.5 % gene sequence similarity. In other micro-organisms, the gene coding for the β-subunit of RNA polymerase (rpoB) has been shown to be more discriminating than 16S rRNA genes. In this study, rpoB sequences from Bacteriovorax isolates were analysed to determine whether the results would be consistent with those based on 16S rRNA gene sequences. A 1242 bp region of the rpoB gene from 74 saltwater Bacteriovorax strains and two freshwater isolates, Bacteriovorax stolpii Uki2T and Peredibacter starrii A3.12T, was amplified by PCR and analysed. The sequences were aligned and phylogenetic trees were constructed using a neighbour-joining algorithm. The resulting tree showed that the rpoB sequences produced smaller subdivisions of isolates, but were nevertheless consistent with the clusters determined using 16S rRNA gene sequences. Thus, the highly conserved 16S rRNA gene sequences provided good phylogenetic information and the rpoB gene sequences permitted greater differentiation in order to further subdivide phylogenetically distinct groups within the genus Bacteriovorax. Also, on the basis of the extensive diversity and large distance between the saltwater members of the genus Bacteriovorax and the freshwater/soil Bacteriovorax, a reclassification of Bacteriovorax stolpii as Bacteriolyticum stolpii gen. nov., comb. nov. is proposed. A new family, Peredibacteraceae fam. nov., is also described.
-
-
Volumes and issues
-
Volume 74 (2024)
-
Volume 73 (2023)
-
Volume 72 (2022 - 2023)
-
Volume 71 (2020 - 2021)
-
Volume 70 (2020)
-
Volume 69 (2019)
-
Volume 68 (2018)
-
Volume 67 (2017)
-
Volume 66 (2016)
-
Volume 65 (2015)
-
Volume 64 (2014)
-
Volume 63 (2013)
-
Volume 62 (2012)
-
Volume 61 (2011)
-
Volume 60 (2010)
-
Volume 59 (2009)
-
Volume 58 (2008)
-
Volume 57 (2007)
-
Volume 56 (2006)
-
Volume 55 (2005)
-
Volume 54 (2004)
-
Volume 53 (2003)
-
Volume 52 (2002)
-
Volume 51 (2001)
-
Volume 50 (2000)
-
Volume 49 (1999)
-
Volume 48 (1998)
-
Volume 47 (1997)
-
Volume 46 (1996)
-
Volume 45 (1995)
-
Volume 44 (1994)
-
Volume 43 (1993)
-
Volume 42 (1992)
-
Volume 41 (1991)
-
Volume 40 (1990)
-
Volume 39 (1989)
-
Volume 38 (1988)
-
Volume 37 (1987)
-
Volume 36 (1986)
-
Volume 35 (1985)
-
Volume 34 (1984)
-
Volume 33 (1983)
-
Volume 32 (1982)
-
Volume 31 (1981)
-
Volume 30 (1980)
-
Volume 29 (1979)
-
Volume 28 (1978)
-
Volume 27 (1977)
-
Volume 26 (1976)
-
Volume 25 (1975)
-
Volume 24 (1974)
-
Volume 23 (1973)
-
Volume 22 (1972)
-
Volume 21 (1971)
-
Volume 20 (1970)
-
Volume 19 (1969)
-
Volume 18 (1968)
-
Volume 17 (1967)
-
Volume 16 (1966)
-
Volume 15 (1965)
-
Volume 14 (1964)
-
Volume 13 (1963)
-
Volume 12 (1962)
-
Volume 11 (1961)
-
Volume 10 (1960)
-
Volume 9 (1959)
-
Volume 8 (1958)
-
Volume 7 (1957)
-
Volume 6 (1956)
-
Volume 5 (1955)
-
Volume 4 (1954)
-
Volume 3 (1953)
-
Volume 2 (1952)
-
Volume 1 (1951)
Most Read This Month


