 -
Volume 58,
Issue 2,
2008
-
Volume 58,
Issue 2,
2008
Volume 58, Issue 2, 2008
- Notification List
-
-
-
Notification that new names and new combinations have appeared in volume 57, part 11, of the IJSEM
More LessThis listing of names published in a previous issue of the IJSEM is provided as a service to bacteriology to assist in the recognition of new names and new combinations. This procedure was proposed by the Judicial Commission [Minute 11(ii), Int J Syst Bacteriol 41 (1991), p. 185]. The names given herein are listed according to the Rules of priority (i.e. page number and order of valid publication of names in the original articles). Taxonomic opinions included in this List (i.e. the creation of synonyms or the emendation of circumscriptions) cannot be considered as validly published nor, in any other way, approved by the International Committee on Systematics of Prokaryotes and its Judicial Commission.
-
-
- New Taxa
-
- Actinobacteria
-
-
Actinomycetospora chiangmaiensis gen. nov., sp. nov., a new member of the family Pseudonocardiaceae
More LessA novel actinomycete strain, YIM 0006T, was isolated from soil of a tropical rainforest in northern Thailand. The isolate displayed the following characteristics: aerial mycelium is absent, short spore chains are formed directly on the substrate mycelium, contains meso-diaminopimelic acid, arabinose and galactose (cell-wall chemotype IV), the diagnostic phospholipid is phosphatidylcholine, MK-9(H4) is the predominant menaquinone and the G+C content of the genomic DNA is 69.0 mol%. Phylogenetic analysis and phenotypic characteristics showed that strain YIM 0006T belongs to the family Pseudonocardiaceae but can be distinguished from representatives of all genera classified in the family. The novel genus and species Actinomycetospora chiangmaiensis gen. nov., sp. nov. are proposed, with strain YIM 0006T (=CCTCC AA 205017T =DSM 45062T) as the type strain of Actinomycetospora chiangmaiensis.
-
-
-
Microbacterium ginsengisoli sp. nov., a β-glucosidase-producing bacterium isolated from soil of a ginseng field
More LessStrain Gsoil 259T, a β-glucosidase-producing bacterium, was isolated from a soil sample from a ginseng field in the Republic of Korea and characterized in order to determine its taxonomic position. Cells were Gram-positive, heterotrophic, strictly aerobic, non-motile short rods. 16S rRNA gene sequence analysis revealed that strain Gsoil 259T belonged to the genus Microbacterium and was closely related to Microbacterium arborescens IFO 3750T (98.5 %) and Microbacterium imperiale IFO 12610T (97.9 %). However, it has low values for DNA–DNA relatedness with the above strains (20.7 and 17.5 %, respectively). Strain Gsoil 259T possessed chemotaxonomic markers that were consistent with classification in the genus Microbacterium, i.e. MK-11 and MK-12 were the major menaquinones and anteiso-C17 : 0, anteiso-C15 : 0 and iso-C16 : 0 were the predominant cellular fatty acids. The DNA G+C content was 69.4 mol%. The cell-wall sugar was rhamnose and the diamino acid in the cell-wall peptidoglycan was ornithine. On the basis of data from this polyphasic study, strain Gsoil 259T represents a novel species of the genus Microbacterium, for which the name Microbacterium ginsengisoli sp. nov. is proposed. The type strain is Gsoil 259T (=KCTC 19189T =DSM 18659T).
-
-
-
Nocardioides hankookensis sp. nov., isolated from soil
More LessA Gram-positive, non-motile, rod-shaped bacterial strain, DS-30T, was isolated from soil from Dokdo, Korea, and its taxonomic position was investigated by means of a polyphasic study. Strain DS-30T grew optimally at pH 6.0–7.0 and 25 °C in the presence of 0–0.5 % (w/v) NaCl. A phylogenetic analysis based on 16S rRNA gene sequences showed that strain DS-30T fell within the genus Nocardioides, forming a coherent cluster with the type strains of Nocardioides aquiterrae and Nocardioides pyridinolyticus, with which it exhibited 16S rRNA gene sequence similarity values of 98.1 and 98.3 %, respectively. Strain DS-30T exhibited 16S rRNA gene sequence similarity values below 96.8 % with respect to the type strains of the other Nocardioides species. The chemotaxonomic properties of strain DS-30T were consistent with those of the genus Nocardioides: the cell-wall peptidoglycan type was based on ll-diaminopimelic acid, the predominant menaquinone was MK-8(H4) and the major fatty acids were iso-C16 : 0, C17 : 1 ω8c and C18 : 1 ω9c. The DNA G+C content was 71.3 mol%. Strain DS-30T exhibited DNA–DNA relatedness levels of 19 and 22 % with respect to the type strains of N. aquiterrae and N. pyridinolyticus, respectively, and could be differentiated from these species with reference to a number of phenotypic characteristics. On the basis of the data obtained, strain DS-30T represents a novel species of the genus Nocardioides, for which the name Nocardioides hankookensis sp. nov. is proposed. The type strain is DS-30T (=KCTC 19246T =CCUG 54522T).
-
-
-
Kribbella hippodromi sp. nov., isolated from soil from a racecourse in South Africa
More LessA novel actinomycete, designated strain S1.4T, was isolated from a soil sample collected from Kenilworth Racecourse in the Western Cape, South Africa. The strain was able to grow in the presence of 5 % NaCl. It contained ll-diaminopimelic acid and glycine in the cell-wall peptidoglycan with glucose present in the whole-cell sugar profile. Strain S1.4T was shown to be a member of either the genus Kribbella or the genus Nocardioides based on a rapid molecular identification method by using single-enzyme restriction endonuclease digestion of the PCR-amplified 16S rRNA gene with MboI, VspI, SphI, SnaBI, SalI and AgeI. Analysis of the 16S rRNA gene sequence indicated that strain S1.4T belonged to the genus Kribbella. Phylogenetic analysis based on 16S rRNA gene sequence comparisons showed that strain S1.4T was related most closely to Kribbella solani DSA1T. Strain S1.4T was phenotypically distinct from K. solani DSA1T and was shown to be a separate genomic species based on DNA–DNA hybridization experiments (40.4±3.8 % DNA–DNA relatedness between the two). Strain S1.4T (=DSM 19227T =NRRL B-24553T) is thus presented as the type strain of a novel species, for which the name Kribbella hippodromi sp. nov. is proposed.
-
-
-
Mycobacterium setense sp. nov., a Mycobacterium fortuitum-group organism isolated from a patient with soft tissue infection and osteitis
More LessA Gram-positive, rod-shaped acid-fast bacterium was isolated from a patient with a post-traumatic chronic skin abscess associated with osteitis. Morphological analysis, 16S rRNA, hsp65, sodA and rpoB gene sequence analysis, cell-wall fatty acid and mycolic acid composition analyses and biochemical tests showed that the isolate, designated ABO-M06T, belonged to the genus Mycobacterium. Its phenotype was unique and genetic and phylogenetic findings suggest that strain ABO-M06T represents a novel species within the Mycobacterium fortuitum group. The name Mycobacterium setense sp. nov. is proposed for this novel species, with the type strain ABO-M06T (=CIP 109395T=DSM 45070T).
-
-
-
Brevibacterium marinum sp. nov., isolated from seawater
More LessA novel yellow-pigmented actinobacterium was isolated from seawater collected from Hwasun Beach in Jeju, Republic of Korea. A comparative analysis of the 16S rRNA gene sequence indicated that the organism, designated HFW-26T, was closely related to members of the genus Brevibacterium. As found for other species of the genus Brevibacterium, strain HFW-26T possessed meso-diaminopimelic acid as the diagnostic cell-wall diamino acid, contained MK-8(H2) as the major menaquinone, contained polar lipids that included diphosphatidylglycerol, phosphatidylglycerol, phosphatidylinositol and an unknown phospholipid, and had anteiso-C15 : 0 and anteiso-C17 : 0 as the predominant fatty acids. The G+C content of the DNA was 71.4 mol%. The phylogenetically closest relative was Brevibacterium picturae DSM 16132T (99.0 % 16S rRNA gene sequence similarity). However, DNA–DNA hybridization of strain HFW-26T showed 35.1–43.7 % relatedness with respect to B. picturae DSM 16132T. The novel isolate could be clearly distinguished from B. picturae DSM 16132T on the basis of some cultural, physiological and biochemical characteristics. A battery of phenotypic and genetic data obtained in this study suggest that strain HFW-26T represents a novel species of the genus Brevibacterium, for which the name Brevibacterium marinum sp. nov. is proposed. The type strain is HFW-26T (=JBRI 2001T=KCTC 19221T=DSM 18964T).
-
- Bacteroidetes
-
-
Gaetbulibacter marinus sp. nov., isolated from coastal seawater, and emended description of the genus Gaetbulibacter
More LessA Gram-negative, yellow-coloured, chemoheterotrophic, non-motile, strictly aerobic, rod-shaped bacterium, designated IMCC1914T, was isolated from coastal surface seawater of the Yellow Sea, Korea. The temperature, pH and NaCl ranges for growth were 3–37 °C, pH 8.0–11.0 and 0.5–4.0 %. The DNA G+C content of the strain was 38.1 mol% and the major cellular fatty acids were iso-C15 : 1 (32.1 %), iso-C15 : 0 (20.6 %) and iso-C17 : 0 3-OH (7.8 %). Phylogenetic analysis based on 16S rRNA gene sequences indicated that strain IMCC1914T was related most closely to Gaetbulibacter saemankumensis SMK-12T, with a sequence similarity of 96.2 %. On the basis of phylogenetic data and several distinct phenotypic characteristics, strain IMCC1914T (=KCCM 42380T =NBRC 102040T) could be assigned to the genus Gaetbulibacter as the type strain of a novel species, for which the name Gaetbulibacter marinus sp. nov. is proposed. In addition, an emended description of the genus Gaetbulibacter is presented.
-
-
-
Diversity of Capnocytophaga species in children and description of Capnocytophaga leadbetteri sp. nov. and Capnocytophaga genospecies AHN8471
More LessBacteria of the genus Capnocytophaga form part of the resident oral flora in children and adults. They are recognized as opportunistic pathogens of various extra-oral infections. The significance of individual species in periodontal and extra-oral diseases is unclear, due to the inability of conventional phenotypic tests to identify clinical isolates to species level. Aiming at a clear distinction between species, we undertook a phylogenetic study of a collection of 102 Capnocytophaga strains including 62 oral isolates from children and 40 reference strains from oral and extra-oral infections representing the five known, human, oral Capnocytophaga species. The phylogeny was estimated on the basis of multilocus enzyme electrophoresis (MLEE) of 12 intracellular, housekeeping enzymes and by partial 16S rRNA gene sequencing, and was compared to phenotypic characteristics. The clustering profiles in the MLEE and sequence-based dendrograms were concordant and allowed identification of isolates to species level, based on co-clustering with reference strains. The study confirmed Capnocytophaga ochracea and Capnocytophaga sputigena as separate species, and underlined the problems of distinguishing between them by conventional phenotypic tests. The presence of two distinct clusters of oral isolates from children indicated the existence of novel species, supported by analysis of near-full-length 16S rRNA gene sequences and by DNA–DNA hybridization results. One cluster of weakly saccharolytic isolates without the ability to ferment sucrose is proposed as Capnocytophaga leadbetteri sp. nov. (type strain AHN8855T=CCUG 51857T=NCTC 13375T). Another cluster not phenotypically distinguishable from C. ochracea and C. sputigena is designated Capnocytophaga genospecies AHN8471 (represented by strain AHN8471=CCUG 51856=NCTC 13374).
-
-
-
Parapedobacter soli sp. nov., isolated from soil of a ginseng field
More LessStrain DCY14T, a Gram-negative, non-spore-forming, rod-shaped, non-motile bacterium, was isolated from soil from a ginseng field in Korea and was characterized in order to determine its taxonomic position. 16S rRNA gene sequence analysis revealed that strain DCY14T belongs to the family Sphingobacteriaceae, the highest degree of sequence similarity being found with respect to Parapedobacter koreensis Jip14T (95.8 %). Chemotaxonomic data revealed that strain DCY14T possesses MK-7 as the major menaquinone. The major fatty acids present were anteiso-C13 : 0, iso-C15 : 0, iso-C17 : 0 3-OH and summed feature 4 (C16 : 1 ω7c/iso-C15 : 0 2-OH). The results of physiological and biochemical tests clearly demonstrated that strain DCY14T represents a distinct species. On the basis of these data, DCY14T represents a novel species of the genus Parapedobacter, for which the name Parapedobacter soli sp. nov. is proposed. The type strain is DCY14T (=KCTC 12984T =LMG 24069T).
-
-
-
Bacteroides propionicifaciens sp. nov., isolated from rice-straw residue in a methanogenic reactor treating waste from cattle farms
More LessTwo strictly anaerobic bacterial strains (SV434T and S562) were isolated from rice-straw residue in a methanogenic reactor treating waste from cattle farms in Japan. They had identical 16S rRNA gene sequences and showed almost the same phenotypic properties. The cells of both strains were Gram-negative, non-motile, non-spore-forming rods; extraordinarily long rods often occurred. Remarkable stimulation of growth occurred with the addition of haemin and cobalamin (vitamin B12) to the medium. The supplementary cobalamin and haemin could be replaced if autoclaved and clarified sludge fluid obtained from the reactor was added. Both strains utilized a range of growth substrates, including arabinose, fructose, galactose, glucose, mannose, cellobiose, maltose, glycogen, starch, dextrin, amygdalin, lactate and pyruvate. Both strains produced acetate and propionate with a small amount of succinate from these substrates in the presence of haemin and cobalamin. Both strains were slightly alkaliphilic, having a pH optimum at about 7.9. The temperature range for growth was 5–35 °C, the optimum being 30 °C. The NaCl concentration range for growth was 0–4 % (w/v). Catalase activity was not detected in cells cultivated without haemin, whereas cells cultivated with haemin usually had the enzyme activity. Oxidase and nitrate-reducing activities were not detected. Aesculin was hydrolysed, but gelatin was not hydrolysed. Both strains were sensitive to bile acids. The major cellular fatty acids of both strains were anteiso-C15 : 0 and iso-C15 : 0. Menaquinones MK-8(H0) and MK-9(H0) were the major respiratory quinones and the genomic DNA G+C contents were 46.2–47.5 mol%. A phylogenetic analysis based on 16S rRNA gene sequences placed both strains in the phylum Bacteroidetes. Bacteroides coprosuis (isolated from swine-manure storage pits) was the species most closely related to both strains (95.9 % 16S rRNA gene sequence similarity to the type strain). On the basis of the phylogenetic, physiological and chemotaxonomic analyses, strains SV434T and S562 represent a novel species of the genus Bacteroides, for which the name Bacteroides propionicifaciens sp. nov. is proposed. The type strain is SV434T (=JCM 14649T =DSM 19291T).
-
-
-
Salegentibacter salinarum sp. nov., isolated from a marine solar saltern
More LessA bacterial strain, ISL-4T, comprising Gram-negative, non-motile, rod-shaped cells, was isolated from a marine solar saltern of the Yellow Sea in Korea and was subjected to a polyphasic taxonomic investigation. Phenotypically, the strain resembled members of the genus Salegentibacter. It grew optimally at pH 7.0–8.0 and 30 °C and in the presence of 8 % (w/v) NaCl. It contained MK-6 as the predominant menaquinone. The major fatty acids were iso-C15 : 0 and anteiso-C15 : 0. The DNA G+C content was 37.9 mol%. A phylogenetic analysis based on 16S rRNA gene sequences showed that strain ISL-4T belonged to the genus Salegentibacter, exhibiting sequence similarity values of 95.9–98.6 % with respect to the type strains of recognized Salegentibacter species (with the exception of Salegentibacter catena). Low DNA–DNA relatedness values and differential phenotypic properties, together with its phylogenetic distinctiveness, demonstrated that strain ISL-4T represents a novel species of the genus Salegentibacter, for which the name Salegentibacter salinarum sp. nov. is proposed. The type strain is ISL-4T (=KCTC 12975T =CCUG 54354T).
-
-
-
Algoriphagus hitonicola sp. nov., isolated from an athalassohaline lagoon
More LessA Gram-negative, heterotrophic, aerobic, reddish-orange-pigmented, non-spore-forming, non-motile bacterial strain, designated 7-UAHT, was isolated from salty water from the athalassohaline lagoon at El Hito, located in central Spain. The strain grew optimally at 37 °C and pH 7.0 and in the presence of 2.5 % NaCl. A polyphasic taxonomic study was carried out in order to characterize the strain in detail. Phylogenetic analyses based on 16S rRNA gene sequence comparisons indicated that strain 7-UAHT clustered within the branch constituted by species of the genus Hongiella, which were recently transferred to the genus Algoriphagus. Analysis of the polar lipid profile and DNA G+C content also supported placement of strain 7-UAHT within the genus Algoriphagus. On the basis of its phenotypic, chemotaxonomic and phylogenetic distinctiveness, strain 7-UAHT represents a novel species of the genus Algoriphagus, for which the name Algoriphagus hitonicola sp. nov. is proposed. The type strain is 7-UAHT (=CECT 7267T =CCM 7449T).
-
-
-
Reclassification of Salegentibacter catena Ying et al. 2007 as Salinimicrobium catena gen. nov., comb. nov. and description of Salinimicrobium xinjiangense sp. nov., a halophilic bacterium isolated from Xinjiang province in China
More LessA Gram-negative, non-motile and moderately halophilic rod-shaped bacterium, designated strain BH206T, was isolated from a saline lake of Xinjiang province in China. The isolate showed catalase-positive and oxidase-negative reactions and did not reduce nitrate. Phylogenetic analysis based on 16S rRNA gene sequences showed that the isolate was most closely related to [Salegentibacter] catena HY1T with 95.8 % 16S rRNA gene sequence similarity, and formed a tight phyletic group with [Salegentibacter] catena HY1T with a bootstrap value of 99 % within the family Flavobacteriaceae. However, strain BH206T and [Salegentibacter] catena HY1T formed a phyletic lineage distinct from other Salegentibacter species. The 16S rRNA gene sequence similarities of strain BH206T with other related type species were lower than 94.6 %. On the basis of physiological and molecular properties, it is clear that [Salegentibacter] catena should be reclassified in the new genus Salinimicrobium as Salinimicrobium catena gen. nov., comb. nov. (type strain HY1T=CGMCC 1.6101T=JCM 14015T) and that strain BH206T represents a novel species within the genus Salinimicrobium, for which the name Salinimicrobium xinjiangense sp. nov. is proposed. The type strain of Salinimicrobium xinjiangense is BH206T (=KCTC 12883T=DSM 19287T).
-
-
-
Niabella soli sp. nov., isolated from soil from Jeju Island, Korea
More LessA dark yellow-coloured bacterium, JS13-8T, was isolated from a soil sample from Jeju Island, Republic of Korea. The cells were aerobic, Gram-negative, non-motile, short rods (0.5–0.7×0.8–1.4 μm). Growth occurred at 15–35 °C (optimally at 30 °C), at pH 5.0–8.0 (optimally at pH 6.0–7.0) and at 0–1 % NaCl (w/v). Flexirubin pigment was produced. A phylogenetic analysis based on 16S rRNA gene sequences revealed that strain JS13-8T was closely related to Niabella aurantiaca KACC 11698T (95.0 % sequence similarity). The major respiratory quinone system was MK-7 and the predominant cellular fatty acids were iso-C15 : 0, iso-C15 : 1 G, iso-C17 : 0 3-OH and summed feature 3. The DNA G+C content was 45 mol%. On the basis of the phylogenetic, physiological and chemotaxonomic data, strain JS13-8T represents a novel species of the genus Niabella, for which the name Niabella soli sp. nov. is proposed. The type strain is strain JS13-8T (=KACC 12604T=DSM 19437T).
-
-
-
Chryseobacterium soli sp. nov. and Chryseobacterium jejuense sp. nov., isolated from soil samples from Jeju, Korea
More LessTwo yellow-pigmented bacterial strains, JS6-6T and JS17-8T, isolated from soil samples from Jeju, Republic of Korea, were studied to determine their taxonomic positions. The cells of the two bacteria were aerobic, Gram-negative, non-motile, straight rods. 16S rRNA gene sequence analysis indicated that both isolates should be placed in the genus Chryseobacterium of the family Flavobacteriaceae. Their 16S rRNA gene sequences showed similarities of 93.7–97.5 % to those of type strains of the genus Chryseobacterium. The values for DNA–DNA relatedness between both strains and type strains of closely related Chryseobacterium species were below 34 %. The fatty acids of the novel strains were similar to those of species of the genus Chryseobacterium. Both strains had MK-6 as the predominant respiratory quinone. The DNA G+C contents of strains JS6-6T and JS17-8T were 39.9 and 41.4 mol%, respectively. Phylogenetic evidence, together with the DNA–DNA relatedness values and phenotypic characteristics, indicated that strains JS6-6T and JS17-8T represent two novel species of the genus Chryseobacterium, for which the names Chryseobacterium soli sp. nov. and Chryseobacterium jejuense sp. nov., respectively, are proposed. The type strains of Chryseobacterium soli sp. nov. and Chryseobacterium jejuense sp. nov. are JS6-6T (=KACC 12502T=DSM 19298T) and JS17-8T (=KACC 12501T=DSM 19299T), respectively.
-
-
-
Rudanella lutea gen. nov., sp. nov., isolated from an air sample in Korea
More LessAn orange-coloured bacterial strain, designated 5715S-11T, was isolated from an air sample in Suwon, Republic of Korea. The strain was strictly aerobic, Gram-negative, non-spore-forming, non-flagellated and rod-shaped, frequently forming filaments. Growth of the strain was observed at 4–40 °C (optimum, 30 °C), pH 6.0–8.0 (optimum, pH 7.0) and 0–2 % (w/v) NaCl. Phylogenetically, strain 5715S-11T was shown to be a member of the family Spirosomaceae within the phylum Bacteroidetes. Its closest relatives were Spirosoma linguale LMG 10896T (87.9 % 16S rRNA gene sequence similarity) and Larkinella insperata LMG 22510T (86.2 % 16S rRNA gene sequence similarity). Predominant cellular fatty acids were summed feature 3 (C16 : 1 ω7c and/or iso-C15 : 0 2-OH), C16 : 1 ω5c and iso-C15 : 0. Major polar lipids were phosphatidylethanolamine and unknown aminolipids and polar lipids. On the basis of the evidence from this polyphasic study, strain 5715S-11T is considered to represent a novel species of a new genus, for which the name Rudanella lutea gen. nov., sp. nov. is proposed. The type strain of Rudanella lutea is 5715S-11T (=KACC 12603T =DSM 19387T).
-
- Other Bacteria
-
-
Venenivibrio stagnispumantis gen. nov., sp. nov., a thermophilic hydrogen-oxidizing bacterium isolated from Champagne Pool, Waiotapu, New Zealand
More LessA novel thermophilic, hydrogen-oxidizing bacterium, designated strain CP.B2T, was isolated from a terrestrial hot spring in Waiotapu, New Zealand. Cells were motile, slightly rod-shaped, non-spore-forming and Gram-negative. Isolate CP.B2T was an obligate chemolithotroph, growing by utilizing H2 as electron donor and O2 as corresponding electron acceptor. Elemental sulfur (S0) or thiosulfate (
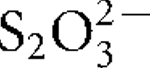 ) was essential for growth. Microbial growth occurred under microaerophilic conditions in 1.0–10.0 % (v/v) O2 [optimum 4–8 % (v/v) O2], between 45 and 75 °C (optimum 70 °C) and at pH values of 4.8–5.8 (optimum pH 5.4). The DNA G+C content was 29.3 mol%. 16S rRNA gene sequence analysis demonstrated that strain CP.B2T belonged to the order Aquificales, with a close phylogenetic relationship to Sulfurihydrogenibium azorense (94 % sequence similarity to the type strain). However, genotypic and metabolic characteristics differentiated the novel isolate from previously described genera of the Aquificales. Therefore, CP.B2T represents a novel species in a new genus, for which the name Venenivibrio stagnispumantis gen. nov., sp. nov. is proposed. The type strain of Venenivibrio stagnispumantis is CP.B2T (=JCM 14244T =DSM 18763T).
) was essential for growth. Microbial growth occurred under microaerophilic conditions in 1.0–10.0 % (v/v) O2 [optimum 4–8 % (v/v) O2], between 45 and 75 °C (optimum 70 °C) and at pH values of 4.8–5.8 (optimum pH 5.4). The DNA G+C content was 29.3 mol%. 16S rRNA gene sequence analysis demonstrated that strain CP.B2T belonged to the order Aquificales, with a close phylogenetic relationship to Sulfurihydrogenibium azorense (94 % sequence similarity to the type strain). However, genotypic and metabolic characteristics differentiated the novel isolate from previously described genera of the Aquificales. Therefore, CP.B2T represents a novel species in a new genus, for which the name Venenivibrio stagnispumantis gen. nov., sp. nov. is proposed. The type strain of Venenivibrio stagnispumantis is CP.B2T (=JCM 14244T =DSM 18763T).
-
-
-
‘Candidatus Phytoplasma omanense’, associated with witches'-broom of Cassia italica (Mill.) Spreng. in Oman
More LessSamples from plants of Cassia italica exhibiting typical witches'-broom symptoms (Cassia witches'-broom; CWB) were examined for the presence of plant pathogenic phytoplasmas by PCR amplification using universal phytoplasma primers. All affected plants yielded positive results. RFLP analyses of rRNA gene products indicated that the phytoplasmas detected were different from those described previously. Phylogenetic analysis of 16S rRNA gene sequences confirmed that CWB represents a distinct lineage and shares a common ancestor with ‘Candidatus Phytoplasma phoenicium’. Molecular comparison revealed that the 16S rRNA gene sequences of the four CWB strains (IM-1, IM-2, IM-3 and IM-4) identified in symptomatic C. italica samples were nearly identical (99.6–100 % similarity). The closest relatives were members of the pigeon pea witches'-broom phytoplasma ribosomal group (16SrIX; 95–97 % sequence similarity). On the basis of unique 16S rRNA gene sequences and biological properties, the phytoplasma associated with witches'-broom of C. italica in Oman represents a coherent but discrete novel phytoplasma, ‘Candidatus Phytoplasma omanense’, with GenBank/DDBJ/EMBL accession number EF666051 representing the reference strain.
-
- Proteobacteria
-
-
Hahella antarctica sp. nov., isolated from Antarctic seawater
More LessA Gram-negative, psychrotolerant, chemoheterotrophic, aerobic, cream-coloured bacterium, designated IMCC3113T, was isolated from coastal seawater from the Antarctic. On the basis of 16S rRNA gene sequence similarity analyses, the strain was most closely related to the type strains of Hahella chejuensis (93.0 %) and Hahella ganghwensis (92.1 %) in the Gammaproteobacteria. Phylogenetic investigations using 16S rRNA gene sequences showed that this Antarctic marine isolate formed a robust monophyletic clade with the two Hahella species but constituted a distinct phyletic line in the clade. The DNA G+C content of strain IMCC3113T was 56.4 mol% and the major respiratory quinone was Q-9. Several phenotypic and physiological characteristics, including the temperature range and NaCl optimum for growth, several enzyme activities and the cellular fatty acid composition, served to differentiate the strain from the two Hahella species. Therefore strain IMCC3113T represents a novel species of the genus Hahella, for which the name Hahella antarctica sp. nov. is proposed. The type strain is IMCC3113T (=KCCM 42675T =NBRC 102683T).
-
Volumes and issues
-
Volume 74 (2024)
-
Volume 73 (2023)
-
Volume 72 (2022 - 2023)
-
Volume 71 (2020 - 2021)
-
Volume 70 (2020)
-
Volume 69 (2019)
-
Volume 68 (2018)
-
Volume 67 (2017)
-
Volume 66 (2016)
-
Volume 65 (2015)
-
Volume 64 (2014)
-
Volume 63 (2013)
-
Volume 62 (2012)
-
Volume 61 (2011)
-
Volume 60 (2010)
-
Volume 59 (2009)
-
Volume 58 (2008)
-
Volume 57 (2007)
-
Volume 56 (2006)
-
Volume 55 (2005)
-
Volume 54 (2004)
-
Volume 53 (2003)
-
Volume 52 (2002)
-
Volume 51 (2001)
-
Volume 50 (2000)
-
Volume 49 (1999)
-
Volume 48 (1998)
-
Volume 47 (1997)
-
Volume 46 (1996)
-
Volume 45 (1995)
-
Volume 44 (1994)
-
Volume 43 (1993)
-
Volume 42 (1992)
-
Volume 41 (1991)
-
Volume 40 (1990)
-
Volume 39 (1989)
-
Volume 38 (1988)
-
Volume 37 (1987)
-
Volume 36 (1986)
-
Volume 35 (1985)
-
Volume 34 (1984)
-
Volume 33 (1983)
-
Volume 32 (1982)
-
Volume 31 (1981)
-
Volume 30 (1980)
-
Volume 29 (1979)
-
Volume 28 (1978)
-
Volume 27 (1977)
-
Volume 26 (1976)
-
Volume 25 (1975)
-
Volume 24 (1974)
-
Volume 23 (1973)
-
Volume 22 (1972)
-
Volume 21 (1971)
-
Volume 20 (1970)
-
Volume 19 (1969)
-
Volume 18 (1968)
-
Volume 17 (1967)
-
Volume 16 (1966)
-
Volume 15 (1965)
-
Volume 14 (1964)
-
Volume 13 (1963)
-
Volume 12 (1962)
-
Volume 11 (1961)
-
Volume 10 (1960)
-
Volume 9 (1959)
-
Volume 8 (1958)
-
Volume 7 (1957)
-
Volume 6 (1956)
-
Volume 5 (1955)
-
Volume 4 (1954)
-
Volume 3 (1953)
-
Volume 2 (1952)
-
Volume 1 (1951)
Most Read This Month


